蒸散作为地气界面水热碳循环的核心变量之一,其准确测算一直是水文气象学的难点问题之一。传统水文气象学蒸散测算方法及遥感反演模型大多存在系数经验性、参数化方案复杂不确定的问题。我校地理与遥感学院潘鑫副教授、杨英宝教授研究组,联合中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所刘元波研究员团队和英国莱斯特大学国家对地观测中心Kevin Tansey教授团队针对上述问题,近日开展科学研究,在蒸散测算及遥感反演方面取得系列研究成果。
团队引入地表能量平衡理论和热力学平衡理论,从哈密顿原理出发在原始非参数化蒸散测算方法(NP方法)的基础上,分别发展了基于地表能量平衡理论的单源和双源非参数化蒸散测算方法(SFE-NP方法和TS-NP方法),方法避免了传统方法的阻抗参数化和系数经验化带来的不确定性,显著改善了原始非参数化方法在干旱区的高估问题,在全球范围的通量站点处验证结果表明其精度可靠。
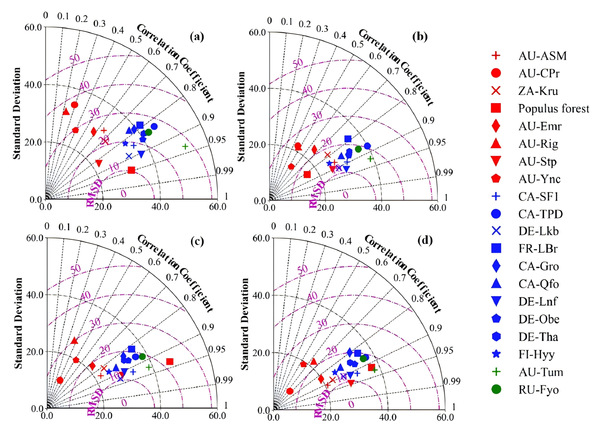
图1 四种方法在全球通量站点处的蒸散测算精度泰勒图(a. NP方法,b. SFE-NP方法,c. RH-PM方法,d. TS-NP方法)
团队比较了输入空间降尺度策略和输出空间降尺度策略对蒸散遥感反演的影响,定量化揭示了以地表温度为代表的模型输入变量空间尺度转换对蒸散反演精度的主导影响,同时明确了地表温度晴空偏差对蒸散遥感反演的影响规律,为高空间分辨率、长时间尺度蒸散可靠反演提供支撑。
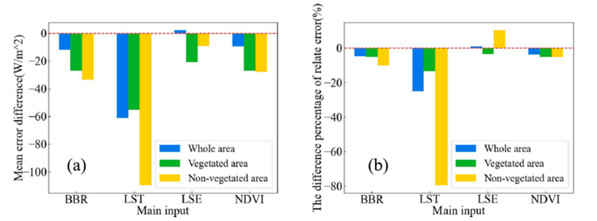
图2 不同输入变量(BBR,宽波段反照率;LST,地表温度;LSE,地表发射率;NDVI,植被指数)空间尺度转换对蒸散遥感反演的误差贡献
在此基础上,团队构建了区域及全球的蒸散遥感反演模型(RSNP模型),并在对输入数据精度校正基础上,生产了2001-2019年多个流域及全球的蒸散遥感产品,产品经过通量站点和流域水量平衡验证,精度可靠,时空连续无缝。
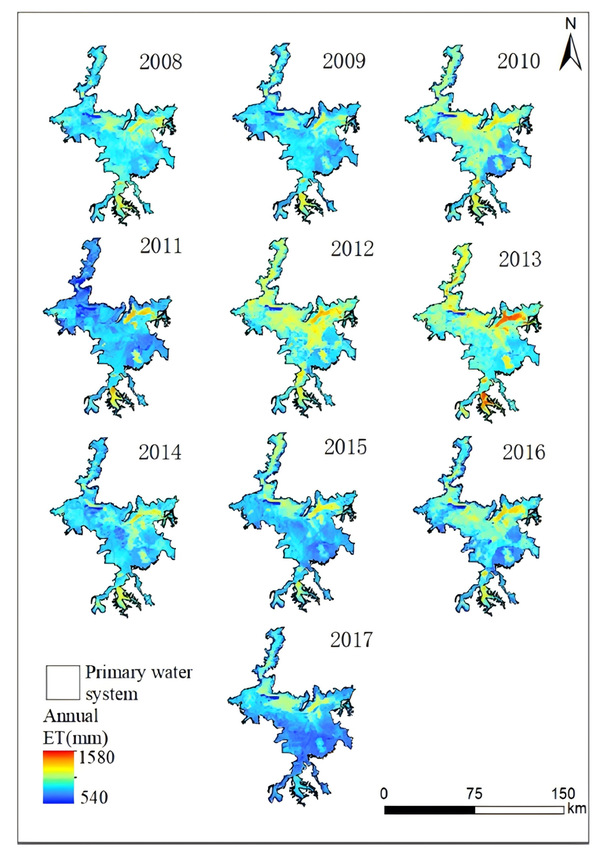
图3 2008-2017年鄱阳湖湿地年蒸散空间分布图
上述研究得到了国家自然科学基金项目(41701487, 42230112, 42071346)等的资助。系列成果发表于《Journal of Hydrology》《International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation》等期刊上,潘鑫副教授为系列论文的第一、通讯作者,河海大学地理与遥感学院杨英宝教授,中国科学院南京地理与湖泊研究所刘元波研究员,英国莱斯特大学国家对地观测中心Kevin Tansey教授为系列论文的合作作者。
代表成果:
1. Pan, X., Yang, Z., Yuan, J., Guluzade, R., Wang, Z., Liu, S., ... & Liu, Y. (2024). A two-source non-parametric method for estimating terrestrial evapotranspiration: Validation at eddy covariance sites. Journal of Hydrology, 645, 132278.
2. Pan, X., Yang, Z., Liu, Y., Yuan, J., Wang, Z., Liu, S., & Yang, Y. (2024). A non-parametric method combined with surface flux equilibrium for estimating terrestrial evapotranspiration: Validation at eddy covariance sites. Journal of Hydrology, 631, 130682.
3. Yang, Z., Pan, X., Liu, Y., Tansey, K., Yuan, J., Wang, Z., ... & Yang, Y. (2024). Evaluation of spatial downscaling for satellite retrieval of evapotranspiration from the nonparametric approach in an arid area. Journal of Hydrology, 628, 130538.
4. Pan, X., Wang, Z., Liu, S., Yang, Z., Guluzade, R., Liu, Y., ... & Yang, Y. (2024). The impact of clear-sky biases of land surface temperature on monthly evapotranspiration estimation. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 129, 103811.
5. Zhou, Y., Pan, X., Yang, Z., Wang, Z., Guluzade, R., Yuan, J., ... & Yang, Y. (2024). The comparison between single-point method and footprint-integrated validation method of the remote-sensing retrieval of evapotranspiration: a case study at Daman site. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1-21.
6. Zhu, H., Yuan, J., Pan, X., Wang, Z., Yang, Z., Ding, X., ... & Yang, Y. (2024). Improving GLASS AVHRR-derived broadband thermal-infrared emissivity (BBE) using GLASS MODIS-derived BBE: A Global Long-Term Study. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters. 3508745.
7. Pan, X., Liu, S., Tansey, K., Fan, X., Yang, Z., Yuan, J., ... & Liu, Y. (2023). Spatio-temporal variation of evapotranspiration and its linkage with environmental factors in the largest freshwater lake wetland in China. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 47, 101424.